Articles
- Intel
- Samsung
- Texas Instruments
- STMicroelectronics
- Infineon
- NXP Semiconductors
- Microchip
- Analog Devices
- onsemi
- Skyworks Solutions
- Avago
- Marvell
- Omnivision Technologies
- ROHM
- Seoul Semiconductor
- Silego
- Cirrus Logic
- Silicon Labs
- Lattice Semiconductor
- Cypress Semiconductor
- Toshiba
- Mitsubishi
- Panasonic
- Sharp
- Omnetics
- Laird
- TDK-Lambda
- WAGO
- All Distributors
What Are MRDIMMs? The Memory Technology Servers Designers Are Discussing
As the demand for data-intensive workloads continues to rise, modern servers are under increasing pressure to match computational power with memory bandwidth. Industries like artificial intelligence, high-performance computing, and real-time analytics rely on memory subsystems capable of delivering data at extraordinarily high speeds to avoid bottlenecks.
While advancements in processor technology have driven exponential gains in computational performance, memory development has struggled to keep pace. Against this backdrop, many leading industry players have started adopting multiplexed rank DIMM (MRDIMM) technology, a new type of memory that offers significant performance improvements.
What Are MRDIMMs?
MRDIMM technology addresses the growing need for higher memory bandwidth in modern servers. As CPU core counts and clock speeds continue to rise, memory must deliver data at rates that keep up with these advancements. MRDIMMs achieve this by operating two memory ranks simultaneously, effectively doubling the data throughput compared to standard DDR5 DIMMs. For example, while DDR5 DIMMs typically support speeds up to 4,800 MT/s, Gen1 MRDIMMs can reach speeds of up to 8,800 MT/s. Future generations are expected to achieve even higher rates, with Gen2 targeting 12,800 MT/s and Gen3 expected to reach 17,600 MT/s.
MRDIMMs use a high-speed multiplexer, or data buffer, to simultaneously read from multiple memory banks and transfer data to the CPU. This sets MRDIMMs apart from memory interleaving, which sequentially processes memory operations across multiple DIMMs. By combining simultaneous bank operations with advanced multiplexing, MRDIMMs deliver significantly faster memory performance.
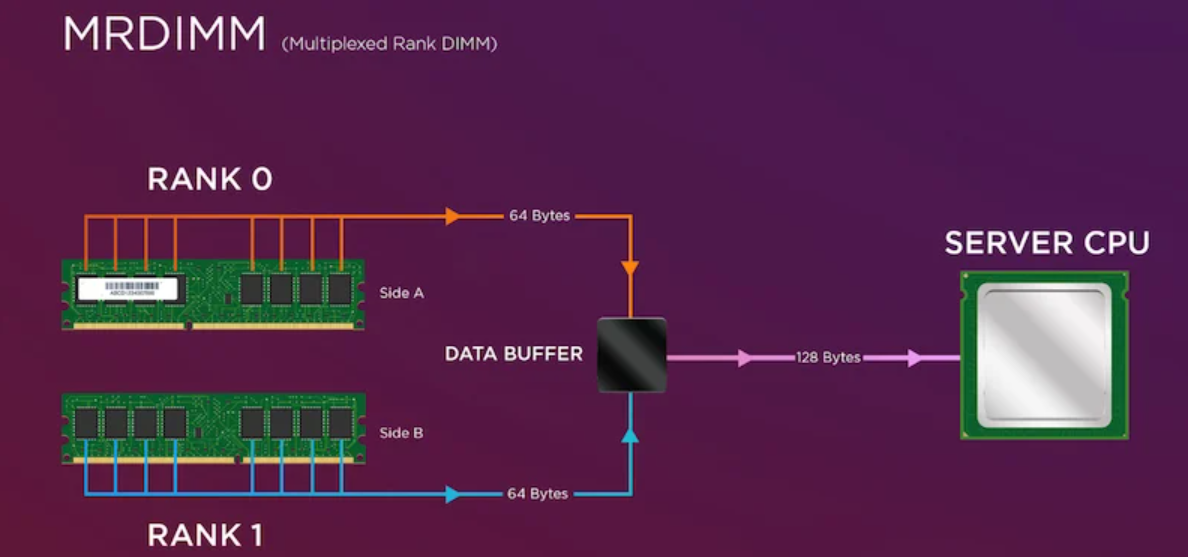
MRDIMM application.
Tall form-factor (TFF) MRDIMMs offer additional benefits by increasing memory capacity without requiring more physical slots. These taller modules accommodate extra memory chips but are designed for larger server architectures, such as 2U or larger systems.
By enabling faster and more efficient data delivery, MRDIMMs help future-proof server designs against the growing demands of high-performance computing.
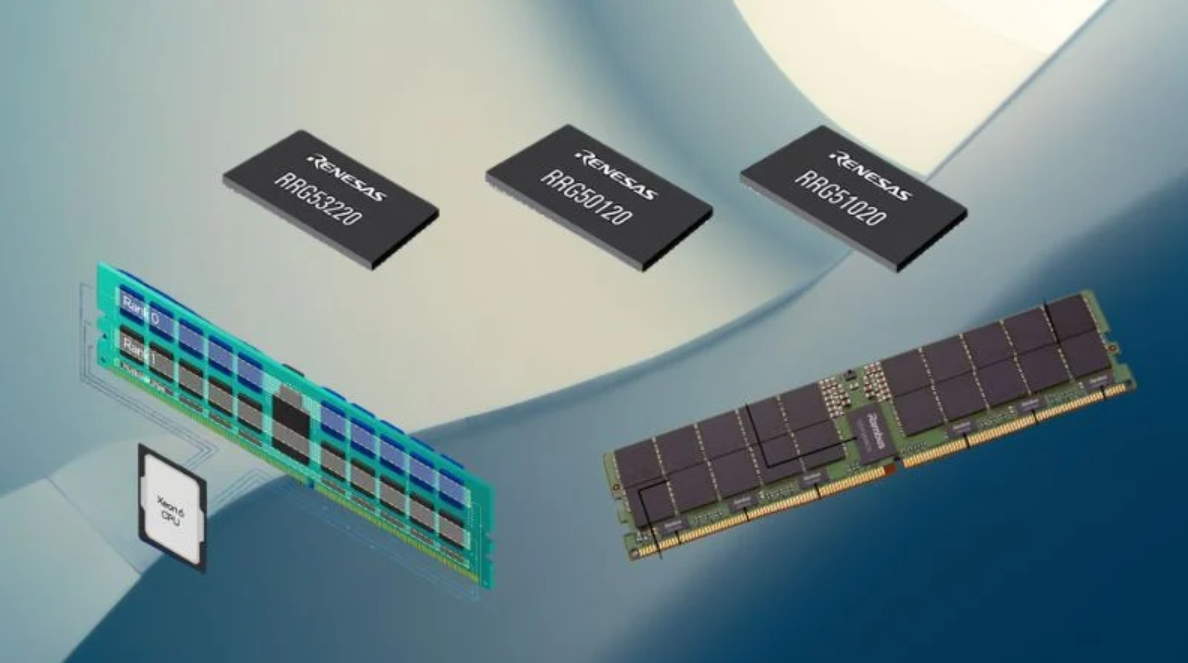
Renesas Launches Complete DDR5 MRDIMM Chipsets
Renesas recently released the industry's first complete chipset solutions for second-generation DDR5 MRDIMMs. These new solutions, which support memory speeds of up to 12,800 MT/s, target AI and high-performance computing workloads that require substantial memory bandwidth.

Renesas’ second-generation MRDIMM solutions.
The solution includes three key components: the RRG50120 multiplexed registered clock driver, the RRG51020 multiplexed data buffer, and the RRG53220 power management integrated circuit (PMIC). The clock driver buffers command and address signals between host controllers and DRAMs, consuming 45% less power than its predecessor. The data buffer boosts throughput by multiplexing data paths, while the PMIC ensures superior power efficiency and protection against electrical overstress.
According to Renesas, these products offer a 1.35x improvement in memory bandwidth compared to first-generation MRDIMMs, with mass production expected in 2025.
Intel’s MRDIMM Technology Boosts Xeon 6 Performance
Intel announced that its newly introduced Xeon 6 processors will support MRDIMM technology. Independent testing has shown that Xeon 6 processors using MRDIMMs achieved up to a 33% performance boost compared to identical systems using traditional RDIMMs.
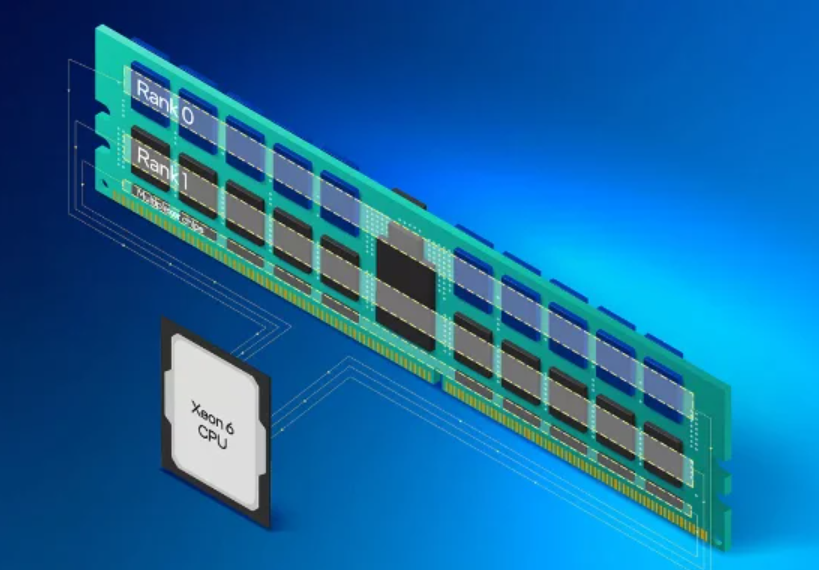
Xeon 6 CPUs will support MRDIMM solutions.
Despite supporting MRDIMMs, these Xeon 6 processors remain compatible with existing RDIMM infrastructure, meaning no changes are required to form factors or server configurations. This ensures data center operators can easily adopt the new technology by simply swapping RDIMMs for MRDIMMs, with no additional hardware adjustments. The integration also retains Xeon 6’s advanced features, including reliability and error-correcting capabilities.
Rambus Unveils DDR5 MRDIMM Chipsets
Rambus has recently unveiled its chipsets for next-generation DDR5 RDIMMs and MRDIMMs, supporting data rates of up to 12,800 MT/s. The suite includes the Gen5 registering clock driver for RDIMMs, as well as the multiplexed registering clock driver and data buffer for MRDIMMs.
The DDR5 MRDIMM architecture uses a single multiplexed registering clock driver and ten multiplexed data buffers per module to efficiently multiplex memory channels. Meanwhile, Rambus' second-generation PMIC delivers high current at low voltages to optimize power efficiency and support more DRAM per module.
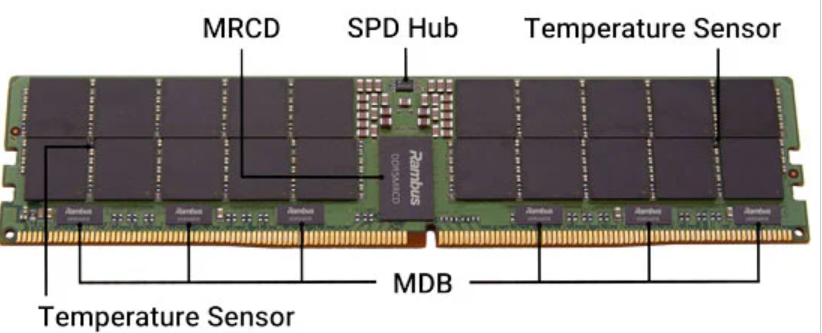
DDR5 MRDIMM concept image.
Like Intel's solutions, Rambus' chipsets maintain compatibility with existing server platforms while also supporting taller MRDIMMs for increased memory capacity in constrained physical spaces.
Higher Bandwidths for Data-Heavy Workloads
The adoption of MRDIMMs could significantly change how memory bottlenecks are addressed in modern data centers. As computing power scales exponentially, data center operators face the challenge of boosting memory performance without overhauling their infrastructure—especially for industries handling large-scale, memory-intensive workloads. As these solutions ramp up production in 2025 and beyond, MRDIMM technology could become a key component in the next generation of server deployments.

